Data Protection Officer (DPO)

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the European Union's (EU) primary privacy law pertaining to personal data. The GDPR requires organizations that process personal data belonging to the residents of the EU to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) as a way to help keep individuals' personal data safe.
This article will cover the circumstances in which a DPO is necessary, what a DPO's responsibilities are, and how to select and appoint a DPO.
Need a Privacy Policy? Our Privacy Policy Generator will help you create a custom policy that you can use on your website and mobile app. Just follow these few easy steps:
- Click on "Start creating your Privacy Policy" on our website.
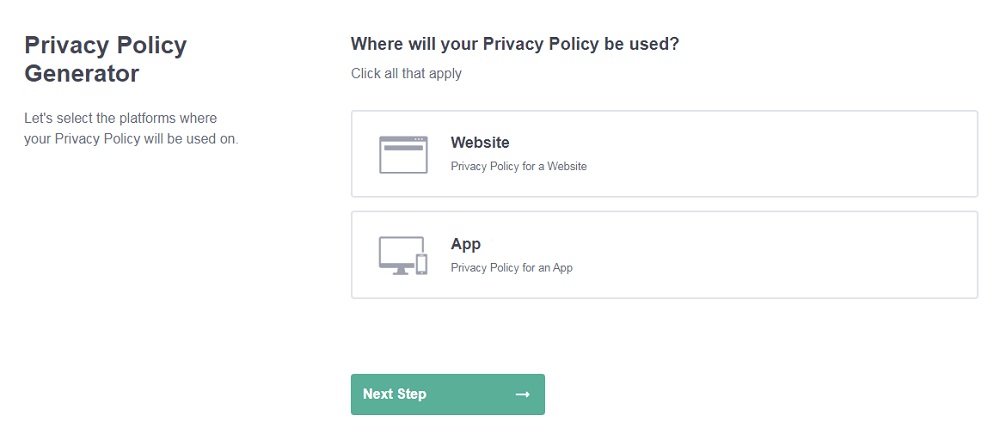
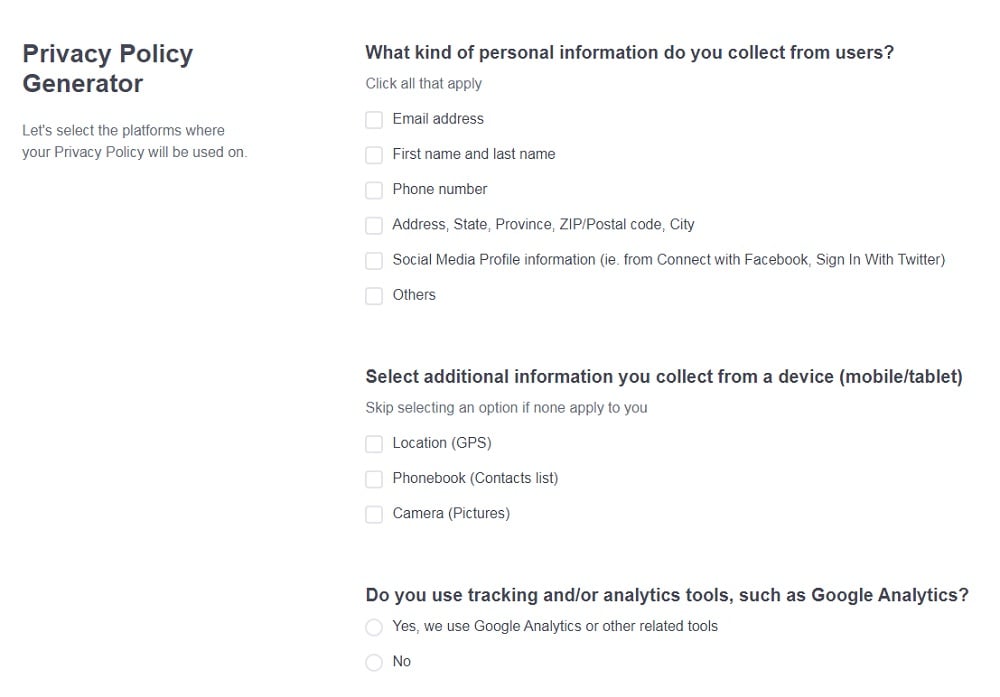
- Select the platforms where your Privacy Policy will be used and go to the next step.
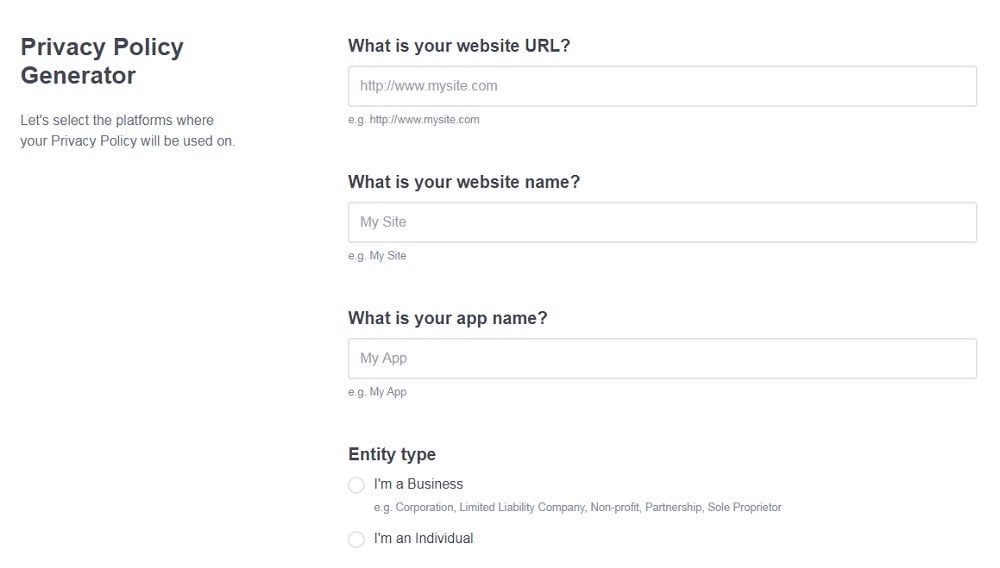
- Add information about your business: your website and/or app.
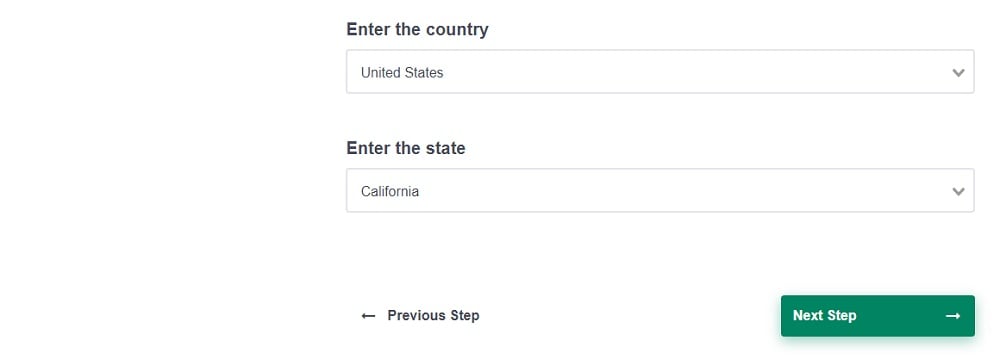
- Select the country:
- Answer the questions from our wizard relating to what type of information you collect from your users.
-
Enter your email address where you'd like your Privacy Policy sent and click "Generate".
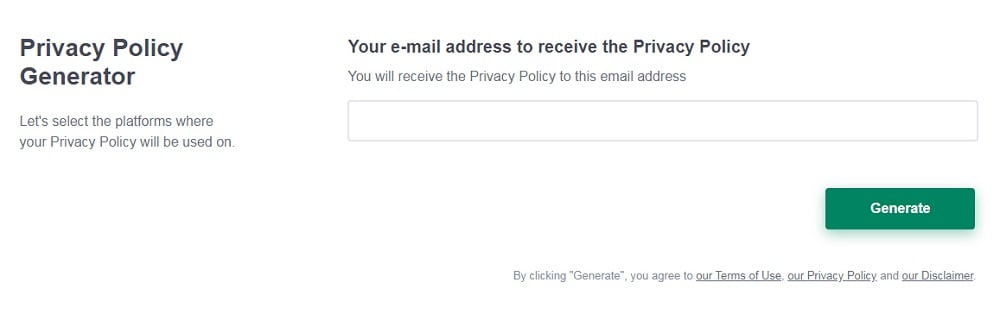
And you're done! Now you can copy or link to your hosted Privacy Policy.
- 1. What is a Data Protection Officer (DPO)?
- 2. When is a Data Protection Officer (DPO) Required?
- 3. Reasons to Have a Data Protection Officer (DPO), Even When Not Required
- 4. What is a Data Protection Officer's Responsibilities?
- 5. How to Select a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
- 6. How to Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
- 7. Summary
What is a Data Protection Officer (DPO)?
A DPO is an individual assigned by an organization to ensure that any personal data the entity collects from individuals is properly handled and kept secure.
DPOs help organizations to comply with the GDPR by helping them implement data protection practices. DPOs are also responsible for conducting security audits and reporting non-compliance to appropriate authorities, amongst other duties and responsibilities.
When is a Data Protection Officer (DPO) Required?

The GDPR requires organizations that meet certain criteria to have a DPO on staff.
It is not the size of an organization that determines whether or not a DPO is required by the GDPR, but the amount and types of data the organization handles, and its reasons for processing it.
DPOs are only required by organizations that handle personal data. The GDPR defines personal data as any information that can be used - alone, or with another piece of information - to identify an individual, such as names, phone and ID numbers, addresses, and health and financial information.
Organizations required to have a DPO include:
- All public bodies (such as colleges, councils, and the police, but not including courts)
- Any organization that controls (makes decisions about how to process) personal data on a large scale
- Any organization that processes personal data (the GDPR's definition of processing data includes collecting, using, and storing personal information) on a large scale
- Organizations that process large amounts of special categories of personal data, including religious beliefs, sexual orientation, genetic data, and race, ethnicity, and health information
- Organizations that process large amounts of data concerning criminal offenses and convictions
Article 37 of the text of the GDPR explains the circumstances in which an organization is required to have a DPO:

Reasons to Have a Data Protection Officer (DPO), Even When Not Required
Having a DPO can provide many benefits to your company, including:
- Helping to make sense of complex privacy legislation
- Helping to protect your company should your business structure or privacy laws change
- Helping to ensure that your business has strong IT security measures in place
- Raising awareness about best data protection practices among both your staff and CEOs
- Functioning as an intermediary between your company and its supervisory authority, as applicable
What is a Data Protection Officer's Responsibilities?

A DPO is responsible for ensuring that an organization handles the personal information it collects in a way that is compliant with the GDPR.
A DPO must have "expert knowledge" of the GDPR's requirements, and is responsible for maintaining an organization's data protection plan, training staff, and conducting security audits on a regular basis.
Article 39 of the GDPR outlines the tasks that a DPO is responsible for. These tasks include:
- Informing and advising data controllers, data processors, and their staff about best data protection practices
- Making sure organizations are compliant with the GDPR
- Training staff who are involved with processing data
- Running regular security audits
- Giving advice and consulting with supervisory authorities about anything having to do with processing data
- Communicating with and reporting GDPR non-compliance to supervisory authorities
How to Select a Data Protection Officer (DPO)

A DPO does not need to have any special training or schooling, but does need to have expert knowledge of the GDPR's requirements and data protection practices. A DPO should have a professional understanding of how data processing and controlling works, and must know how to train staff, advise companies, consult with supervisory authorities, and ensure that an organization is GDPR compliant.
A DPO can be contracted out. A DPO does not need to be obligated to a single organization, and multiple organizations can have the same DPO. Whether you choose to maintain an on-staff DPO or hire a DPO from outside of your organization is up to you.
What's important is that your DPO is available and able to respond to matters concerning data protection when needed, and can independently monitor your company's data protection practices.
It's crucial that you make sure that the person you choose as a DPO does not have any conflicts of interest. For instance, you would not want to hire an attorney who might represent your business in court as your DPO.
The best DPOs will be people who understand the ins and outs of data protection and privacy laws (particularly the GDPR), and who are able to navigate and audit your company's physical, technological, and organizational structures.
Your DPO needs to have no conflict of interest, and be willing and able to report non-compliance to the correct supervisory authorities. The DPO should have excellent organizational, research, and communication skills, and should be proficient in technical security methods.
How to Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)

Once you have chosen an individual to fulfill the role of DPO for your company, you will need to officially appoint them to that role. To appoint a DPO, you should write out a DPO appointment letter, making sure to keep a copy of it in your records.
A DPO appointment letter should contain the following information:
- The names of your organization, the selected DPO, and the DPO's reporting manager
- A description of the DPO's duties
- A notice about the DPO's independence in relation to supervisory instruction
- Signatures from the DPO, representatives, and the organization's managing director
It's important to make sure that you nominate your DPO with a formal letter in order to remain compliant with the GDPR.
Summary
A DPO is a data protection expert who is appointed by an organization to ensure its compliance with the GDPR.
The GDPR requires the following organizations to have a DPO:
- All public bodies
- Any organizations that control or process personal data on a large scale
- Any organizations that control or process large amounts of special categories of data or data concerning criminal convictions or offenses
A DPO is responsible for ensuring an organization's compliance with the GDPR. DPOs train and advise staff and higher-ups, communicate with supervisory authorities, and schedule and implement regular security audits.
An effective DPO should have a deep understanding of data protection practices, superior communication skills, and technological proficiency.
To appoint a DPO, you will need to nominate the individual you have chosen to fulfill the role via an official DPO appointment letter. The DPO appointment letter should contain:
- The name of your organization
- The name of the nominated DPO
- The name of the DPO's reporting manager
- A list of the DPO's obligations
- A notice about the DPO's ability to act independently
- Signatures from the DPO, relevant representatives, and your company's managing director


